In this 21st century, the global economy demands more and more polymaths. Research has shown that people with multiple interests and cross-disciplinary expertise are more likely to be successful. Even employers prefer techies with cross-disciplinary skills.
Hence Mechatronics Engineering which is a combination of different engineering subjects is a new generation course and has a huge potential to grow by leaps and bounds not only in India but also abroad. The aspirants who want to broaden their knowledge in the field of engineering can pursue this course and this course is very ideal for them.
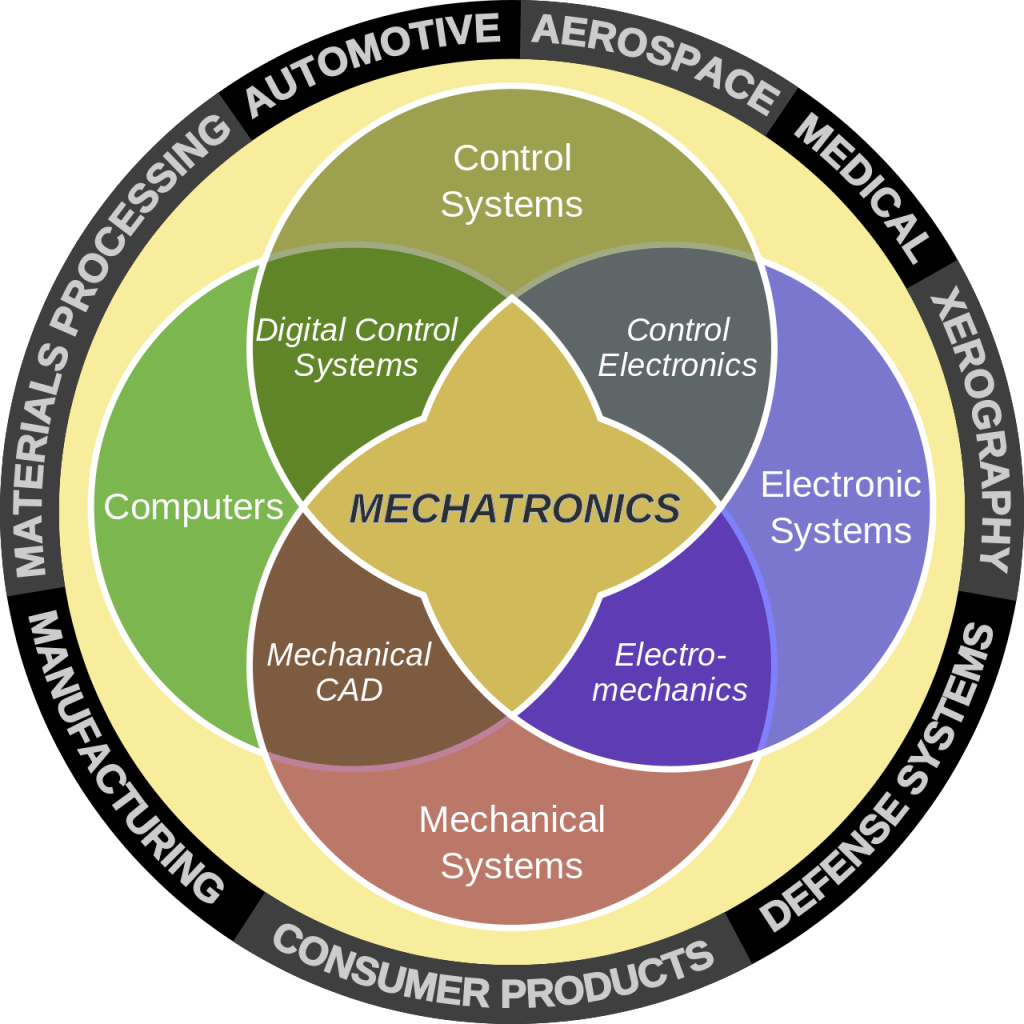
It is hard to find a product in today’s world which is entirely electronic, electrical or mechanical in nature. This means that today’s product is a blend of different engineering subjects. Mechatronics Engineering is a blend of different engineering disciplines and so the demand for Mechatronics Engineers is growing day by day.
Mechatronics is already central to the modern global economy. According to a study by the National Instruments Corporation, machine manufacturers all over the world report having to build machines that are increasingly more complex, yet have less and less time to market those machines. In response to this pressure, most design companies and manufacturers are relying increasingly on mechatronics. According to the Aberdeen Group, a technology think-tank, the most successful companies are the ones that use mechatronics or similar collaborative processes.
Most of the engineering-oriented business and industrial sectors are now paying attention towards Mechatronics Engineering as it has several applications in these sectors. Not only large global enterprises but also smaller innovative companies are hiring Mechatronics Engineers as these industries are inclining towards advanced technologies more and more.
Graduates of Mechatronics Engineering can find employment opportunities in several industries such as Robotics, Nanotechnology, Automation, Aircraft Engineering, Oceanography, Oil and Gas, Biomedical Systems, Transport, and Computer-aided design. Mechatronics is very useful when it comes to automation of industrial tasks.
Mechatronics Engineers design, develop, maintain and manage engineering systems that have the cutting-edge sophisticated technology. Mechatronics Engineering professional plays a key role in areas such as design, research, and development, sales, production management, safety, and quality.
Today’s mechanical devices are composed of electrical, software and mechanical components. These kinds of devices are designed and manufactured by Mechatronics Engineer. Synonymously Mechatronic product is called the smart product, which is a result of the combination of three engineering disciplines namely Electrical, Electronics, Mechanical, and Computer Science & Software Engineering.